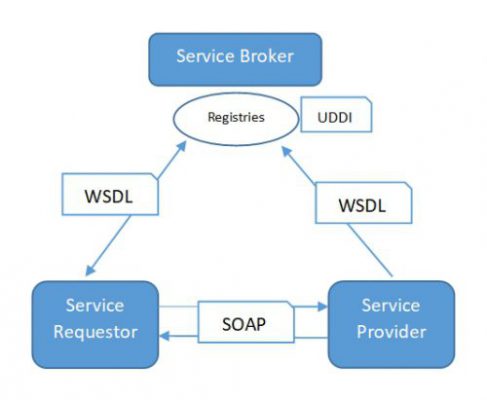
Web services are a method of communication between two computing devices over a network, and the communication happens in standardized ways (and specifications) for the integration of heterogeneous web applications using XML/JSON, SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI. XML/JSON is the data format that provides metadata for the data that it contains; We use SOAP to transfer data; Also, we use WSDL for defining available services as consumable, and UDDI will have the list of services available.
Web services architecture (WSA) mandates the presence of certain characteristics, and suggests a few optional ones, when developing any web service. WSA consists of three significant roles, as you can see in the following diagram, and they are as follow:
- Service Provider
- Service Consumer
- Service Broker

The Service Requestor finds the Service Provider through UDDI, and contacts the provider using the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). The Service Provider then validates the service request and responds to the requestor with XML/JSON as a service response.