Networking Devices, also known as Network Equipment or Computer Networking Hardware, are physical devices which are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data in a computer network. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts or data terminal equipment.
Networking devices may include
- NIC
- Gateways
- Routers
- Network bridges
- Modems
- Switches
- Hubs
- Repeaters
NIC (Network Interface Card)
A Network Interface Card (NIC, also known as a Network Interface Controller, Network Adapter, LAN Adapter or Physical Network Interface, and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
Network interface cards (NICs) provide the interface between cables, discussed in the previous lesson, and computers. This lesson explores the many different types of cards and how their performance affects a network. It also discusses the various connectors used to connect the cards to the cables.
Network interface cards, usually referred to as NICs, act as the physical interface or connection between the computer and the network cable. Figure below shows a NIC with a coaxial-cable connection. The cards are installed in an expansion slot in each computer and server on the network.
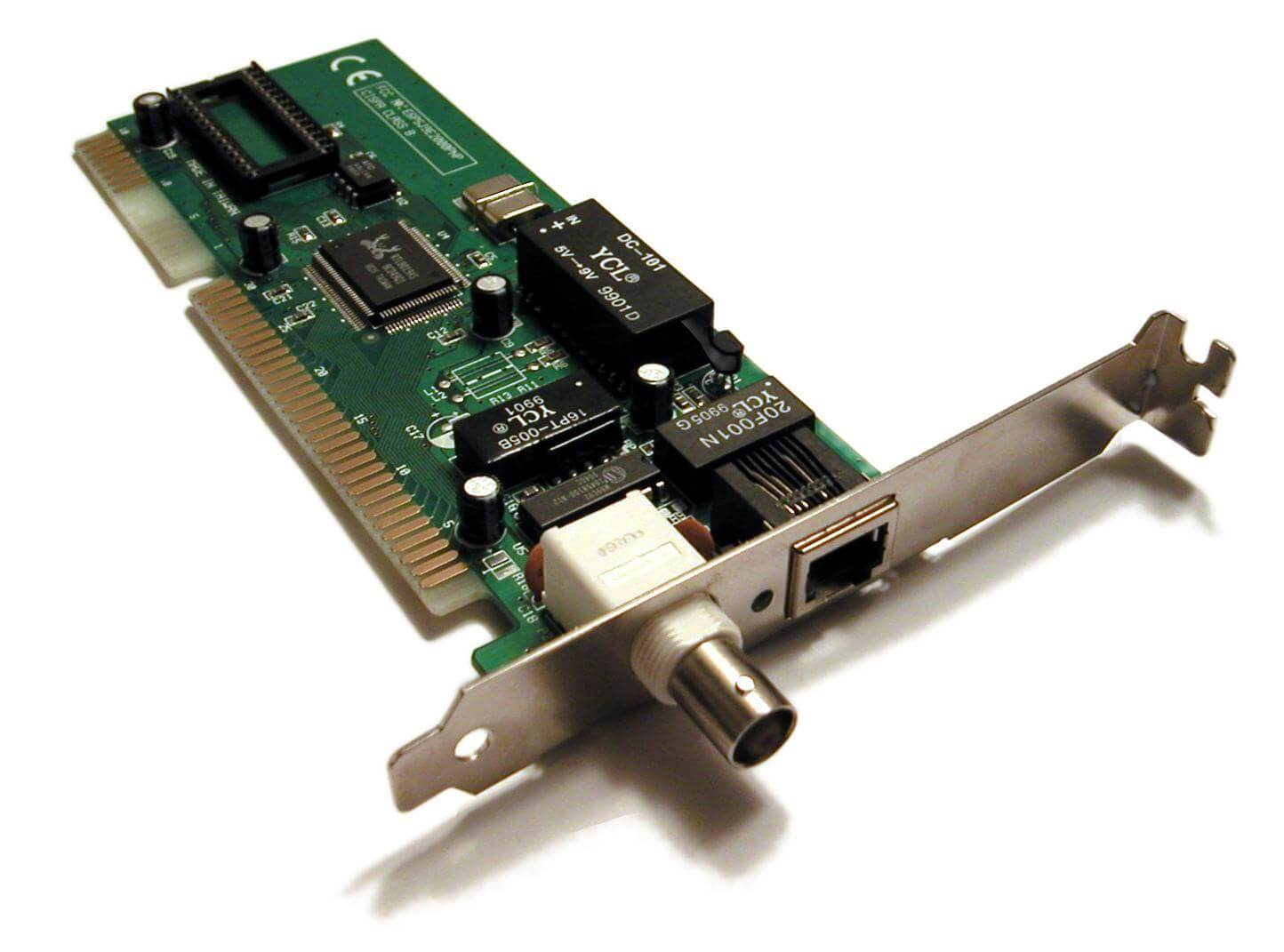
After the NIC has been installed, the network cable is attached to the card’s port to make the actual physical connection between the computer and the rest of the network.
The role of the NIC is to:
- Prepare data from the computer for the network cable.
- Send the data to another computer.
- Control the flow of data between the computer and the cabling system.
- Receive incoming data from the cable and translate it into bytes that can be understood by the computer’s central processing unit (CPU).

